Spring3.2 资源(Resource)管理
可以看到Resource继承自InputStreamSource,该接口定义了getInputStream()方法,用于获取资源对应的输入流对象。Spring中也提供了多种Resource实现,这可以从Resource继承树中看出: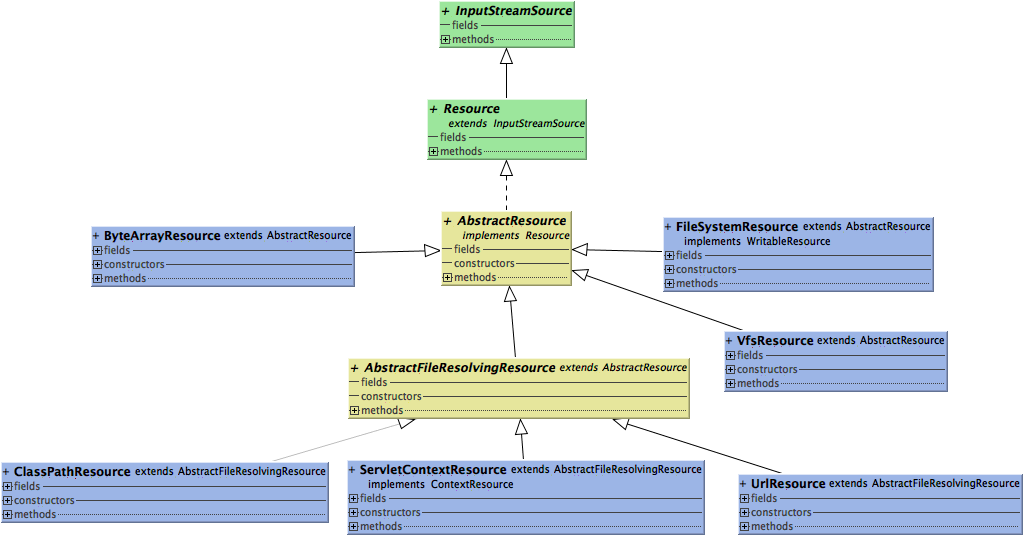

其中有我们比较熟悉的ClasspathResource(类路径资源,Main应用程序常用),FileSystemResource(文件系统资源)等,所有Resource的实现均继承自AbstractResource,其实现了一些基本功能:
public abstract class AbstractResource implements Resource { public boolean exists() { try { // 先从文件系统查看文件是否存在 return getFile().exists(); } catch (IOException ex) { // Fall back to stream existence: can we open the stream? try { InputStream is = getInputStream(); is.close(); return true; } catch (Throwable isEx) { return false; } } } public boolean isReadable() { return true; } public boolean isOpen() { return false; } /** * 需由具体子类实现 */ public URL getURL() throws IOException { throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to URL"); } public URI getURI() throws IOException { URL url = getURL(); try { // URL -> URI return ResourceUtils.toURI(url); } catch (URISyntaxException ex) { throw new NestedIOException("Invalid URI [" + url + "]", ex); } } /** * 需由具体子类实现 */ public File getFile() throws IOException { throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to absolute file path"); } /** * 通过输入流对象读取资源内容长度 */ public long contentLength() throws IOException { InputStream is = this.getInputStream(); Assert.state(is != null, "resource input stream must not be null"); try { long size = 0; byte[] buf = new byte[255]; int read; while ((read = is.read(buf)) != -1) { size += read; } return size; } finally { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException ex) { }